The United Arab Emirates (UAE) will introduce a mandatory, structured e-invoicing system based on the Peppol International Invoice (PINT) on January 1, 2027. With this reform, the Federal Tax Authority (FTA) is significantly advancing the country’s digital transformation.
The aim is to promote transparency, automation, and interoperability in accounting and tax processes, both domestically and in international trade.
In the future, companies will transmit invoices and credit notes in a standardized XML format (PINT AE) to business partners and the FTA in near real time via accredited Peppol service providers.
This will create a modern, interoperable system that strengthens compliance security, efficiency, and digital competitiveness in equal measure.
Background & legal framework
The introduction of electronic invoicing is part of the UAE government’s comprehensive digitalization strategy. The pilot phase will begin on July 1, 2026, followed by a gradual mandatory rollout.
The legal basis is the UAE E-Invoicing Framework, which is based on the international Peppol network. At its heart is the PINT AE format, a country-specific specialization of the international e-invoicing standard.
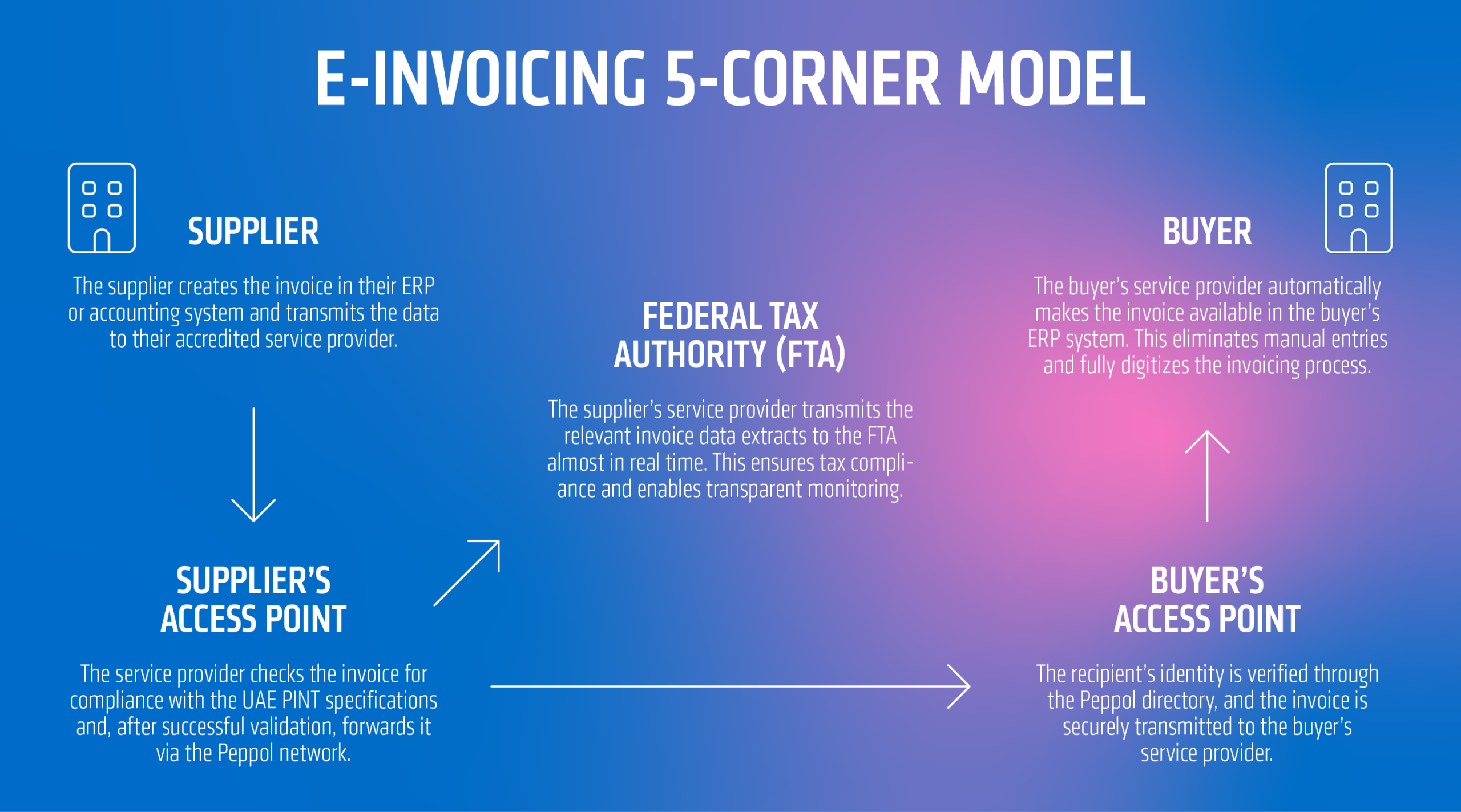
The 5-corner model (DCTCE Framework)
The UAE E-Invoicing Framework is based on the international Peppol network and uses the so-called 5-Corner Model (“Digital Compliance Tax Core Environment – DCTCE”). This model ensures the secure, standardized exchange of electronic invoices between suppliers, buyers, their respective accredited service providers, and the Federal Tax Authority (FTA).
- Corner 1 – Supplier:
The supplier creates the invoice in their ERP or accounting system and transmits the data to their accredited service provider. - Corner 2 – Supplier’s access point:
The service provider checks the invoice for compliance with UAE PINT specifications and, after successful validation, forwards it via the Peppol network. - Corner 3 – Buyer’s access point:
The recipient’s identity is confirmed via the Peppol directory and the invoice is transmitted in encrypted form to the buyer’s service provider. - Corner 4 – Buyer:
The buyer’s service provider automatically makes the invoice available in the buyer’s ERP system.
This eliminates the need for manual entries and completely digitizes the invoicing process. - Corner 5 – Federal Tax Authority (FTA):
The supplier’s service provider transmits relevant invoice data extracts to the FTA in near real time.
This ensures tax compliance and enables transparent monitoring.
The UAE’s 5-corner model is based on the principles of the 4-corner model, which we described in detail in a previous blog article by Aleksandar Lukic and Felix Löffler. Read more about it here.
Unlike some other countries, there is no pre-clearance requirement, i.e., invoices do not have to be approved in advance by the authorities but are sent to business partners and the FTA in parallel.
What is the PINT model?
The Peppol International Invoice (PINT) model is an international e-invoicing format based on the European standard EN 16931 and used worldwide.
It enables electronic invoices to be exchanged between companies, authorities, and countries in a standardized, interoperable, and legally compliant manner.
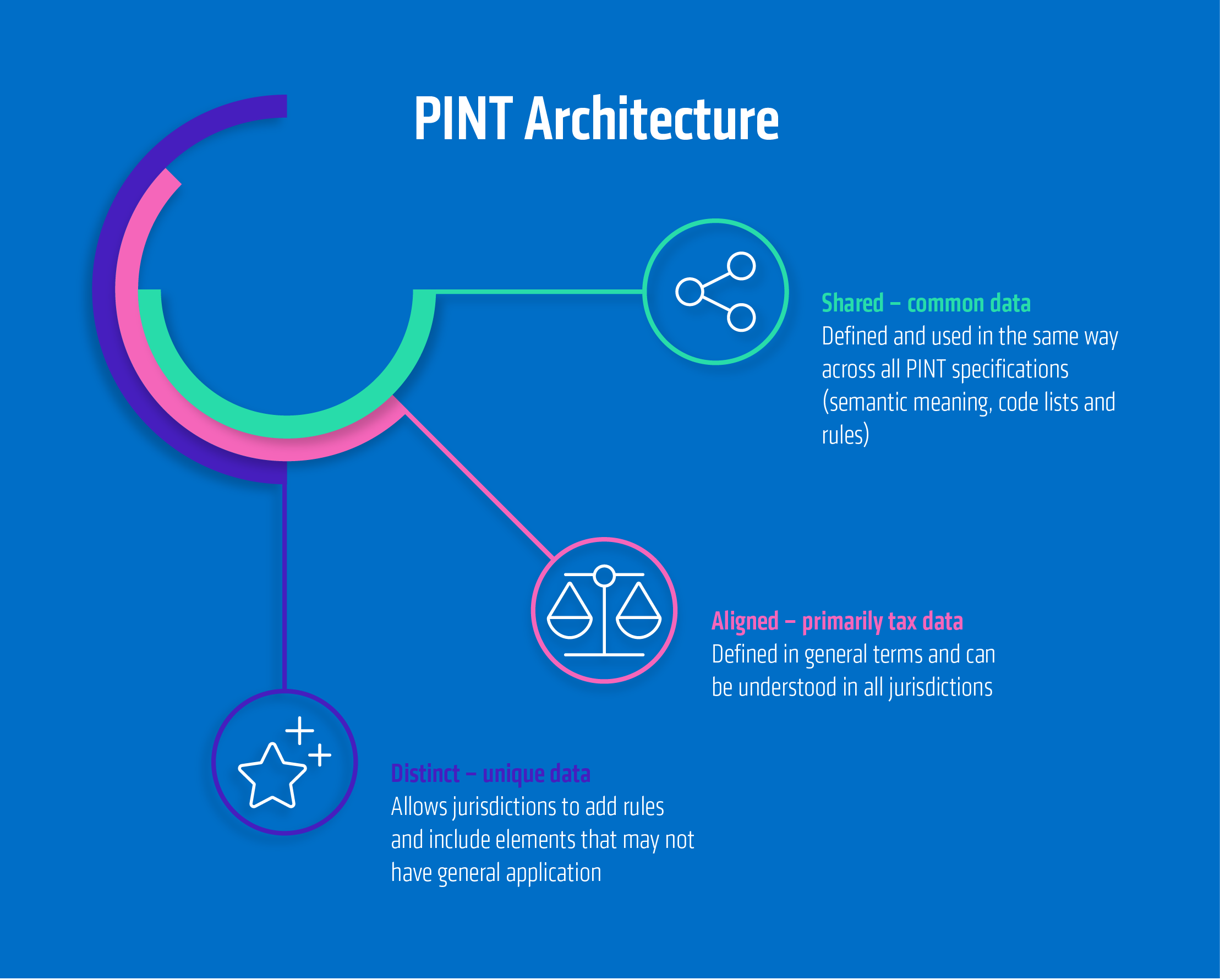
Structure and layer model
The PINT model is divided into three levels:
- Shared Content – universal elements (e.g., invoice number, amount, date)
- Aligned Content – internationally coordinated but locally adaptable concepts (e.g., tax categories, payment terms)
- Distinct Content – country-specific requirements (e.g., UAE VAT rules or free zone information)
Semantic model & business rules
The semantic model defines Data Terms (DT) and Data Groups (DG), to ensure a clear data language.
UAE-specific rules such as IBR-148-AE stipulate, for example, that the VAT number (TIN) must be ten digits long and begin with “1”.
Binding code lists regulate VAT categories, currencies, and billing frequencies.
This standardization enables automatic validation, reconciliation, and posting of invoices, making processes more efficient and reducing errors.
Scope of application & implementation phases in the UAE
The e-invoicing mandate basically affects all companies that conduct B2B or B2G transactions within the UAE.
B2C invoices (to end consumers) are initially exempt, but may follow at a later date.
Implementation will be staggered according to company size and annual turnover for the most recently completed financial year to ensure a smooth introduction.
| Company size / turnover | Start of mandatory implementation |
| Voluntary participation / pilot phase | From July 1, 2026 |
| Large companies (≥ AED 50 million annual turnover) | January 1, 2027 |
| Small and medium-sized enterprises (< AED 50 million) | July 1, 2027 |
This phased approach will enable technical challenges to be identified at an early stage, service providers to be certified, and pilot programs to be carried out.
At the same time, the FTA supports the market with training, compliance tests, and guidelines to assist companies with implementation.
Impact on businesses
The introduction of the e-invoicing system with the PINT model will require technical and organizational adjustments for businesses.
Existing ERP systems (e.g., SAP, Oracle, Microsoft Dynamics) must be supplemented with functions for electronic invoice formats, signatures, and Peppol interfaces.
At the operational level, invoice verification, approval, and archiving will be digitized and automated.
In the long term, companies will benefit from:
- More efficient processes
- Less manual intervention
- Reduced error rate
- Faster payment cycles
The uniform database also improves transparency and traceability vis-à-vis the FTA, which facilitates tax compliance.
It is important that companies define responsibilities at an early stage, train employees, and carry out technical tests to ensure they are ready to go on time.
Advantages of the PINT model for the UAE
With the PINT model, the UAE is relying on an international, interoperable solution that facilitates cross-border trade.
As Peppol is already established in numerous countries, UAE companies benefit from a high level of compatibility and a uniform data standard.
Further advantages:
- Standardized formats reduce errors and data loss
- Automated exchange between companies and authorities
- Increased transparency and digital traceability
- Strengthened international competitiveness
Conclusion
The introduction of the e-invoicing system in the United Arab Emirates marks a decisive step in the digitalization of tax and business processes.
With the PINT AE model, the FTA is creating a system that combines legal certainty, interoperability, and efficiency.
Although the changeover requires short-term investment, it offers significant long-term benefits: standardized processes, less manual work, better compliance, and a stronger competitive position.
Those who act early can use the introduction of e-invoicing not only as an obligation, but as a strategic opportunity to digitize their financial processes.
Companies around the world face similar challenges when introducing digital invoicing and reporting systems. Our experience from numerous e-invoicing and Peppol projects helps to implement such changes in a structured and reliable manner. If you need support with preparation or implementation, we are happy to offer a no-obligation consultation.




