The energy and utilities sector has always been a fast-paced industry that must react flexibly to regulatory changes. Market participants, in particular, need to be adaptable in the area of market communication. With MaCo Cloud (SAP Market Communication for Utilities (MaCo) Cloud), SAP offers a Software-as-a-Service solution as an extension of S/4HANA Utilities, specifically designed for the utilities industry.
The architecture creates a clear separation between the business system and the MaCo Cloud by migrating market communication processes to the cloud. Regulatory requirements and constantly changing data formats are reliably handled by the MaCo Cloud without impacting business processes, thus relieving market partners of the burden of making adjustments.
What are the advantages of system separation?
Since market communication is outsourced to the cloud, regulatory adjustments or changes in communication formats can be implemented centrally by SAP as a service. This means that individual market participants no longer need to adapt their business systems independently when new regulations or standards come into effect. Instead, all necessary updates are implemented centrally. Companies thus benefit from reduced update effort. This not only relieves the burden on IT departments but also minimizes the downtime that often occurs with traditional update processes.
With the SaaS approach, market participants also benefit from the continuous development of the solution. SAP can centrally implement new functionalities or improvements and automatically make them available to all users. This ensures that companies remain compatible with the latest industry standards at all times, without having to independently manage the maintenance and updating of their market communication.
The customer still has the option of running their business system on an on-premise system and making flexible adjustments through so-called enhancement spots. These customization points allow them to integrate their own steps into the processes and thus implement individual business requirements.
What challenges does the MaCo Cloud present?
Despite its advantages, the introduction of the MaCo Cloud also presents challenges that companies should not ignore. A key criticism is the dependence on SAP as the provider, since customizations and changes are entirely under SAP’s control, making companies less flexible. Furthermore, the ongoing costs of the SaaS solution can be higher in the long run than those of an on-premise alternative, especially with intensive use. The limited customization options, despite the provided “Customer Extensions,” can also be problematic for companies with specific requirements.
So how does it all work?
For every process in the business system, there is a parallel process in the cloud that communicates with each other. Process IDs in the business system are marked with a *B* and in the MaCo Cloud system with *C*.

The processes in both the business system and the MaCo Cloud are mapped using the Application Process Engine (APE) framework. All processes and documents are linked via the Common Access Reference (CAR), enabling consistent communication in near real-time and simplifying the identification of related processes. Instead of the previously used iDocs, data transfer now takes place using transfer documents. Transfer documents are structured data sets containing all necessary information in a format defined by SAP – either for further processing in the business system or for transfer to the cloud. From there, the data can be converted into the EDIFACT format required for market communication. This enables standardized data transfer between the systems, specifically tailored to the requirements of market communication.
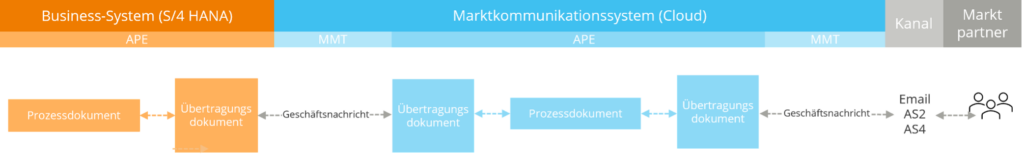
Which processes take place in which system?
All key business processes—such as delivery start, master data changes, and customer transactions—are executed within the business system, while the MaCo Cloud acts as a dedicated market communication system. Here, process-relevant checks, deadline monitoring, and the creation and transmission of EDIFACT messages take place, supported by the middleware component
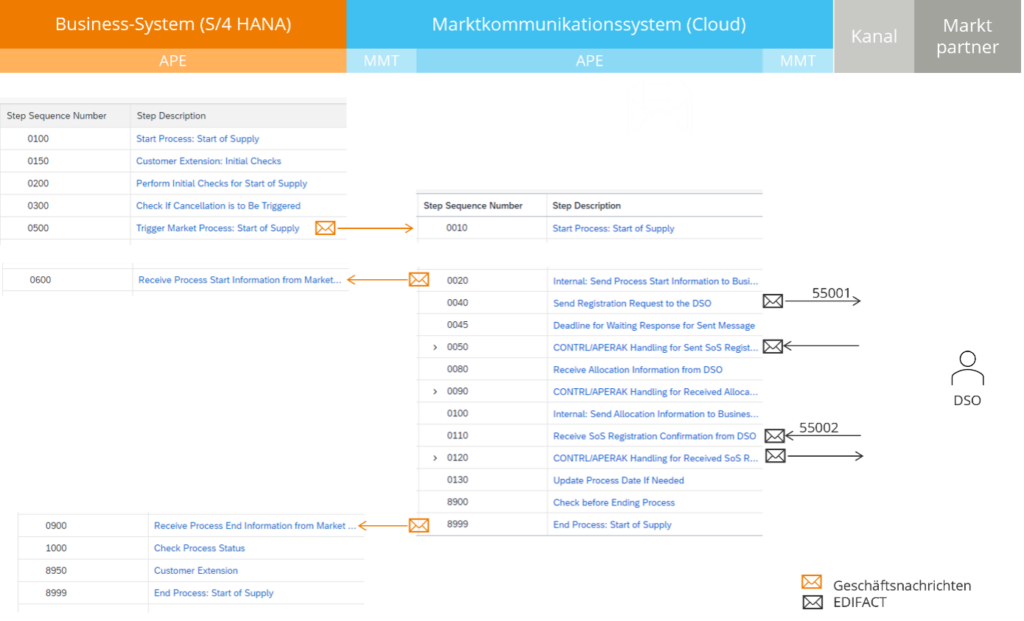
The process begins in the new supplier’s business system when a customer registration is received. A process document is created that records the workflow and the process status. Within the business system, the start of supply initially goes through customer-specific steps, such as checks of contract data or validations. Additionally, it is verified whether the previous supplier needs to deregister with the network operator.
Once these checks are complete, a process is initiated in the MaCo Cloud. The business system sends a corresponding message to the MaCo Cloud, which then triggers the process.
If deregistration of the previous supplier is required, the MaCo Cloud generates the corresponding message to the network operator. The MaCo Cloud handles the entire market communication process, including creating and sending the message in EDIFACT format and managing the responses (CONTRL and APERAK).
If the network operator reports a different delivery start date, this date is automatically adjusted in the MaCo Cloud. The synchronized data is then transferred back to the business system, ensuring that it always has up-to-date and accurate information. The MaCo Cloud already processes the network operator’s feedback in a format understandable to the business system, which significantly reduces integration effort.
The process then continues in the business system. Final checks are carried out there, such as the final validation of the contract data. After successful completion of these checks, the delivery start process is marked as complete.
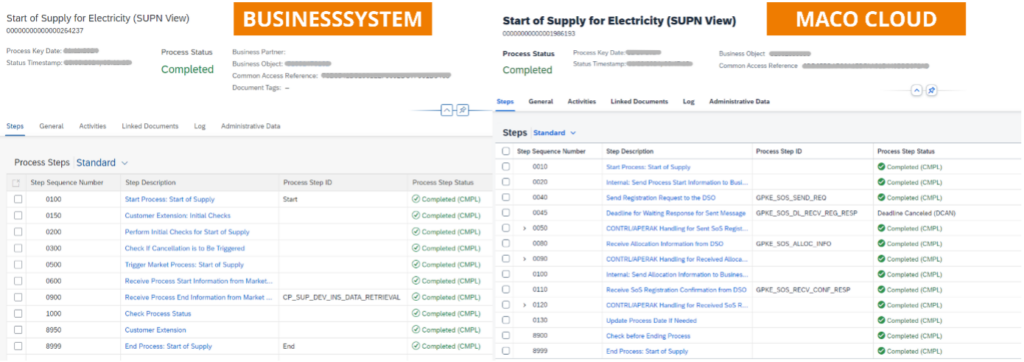
What conclusions can be drawn from this?
In summary, the interplay between the business system and the MaCo Cloud enables efficient and regulatory-compliant processing of business processes in the energy and utilities sector. The clear separation of systems relieves the burden on the business system, while the MaCo Cloud centralizes and automates market communication. This reduces the potential for errors, facilitates adaptation to regulatory changes, and ensures future-proof processing. This model optimizes collaboration between market participants and increases the efficiency of the entire, cross-company process landscape. However, dependence on SAP, ongoing costs, and limited customization options also present challenges.
If you would like to learn more about the possibilities of Maco Cloud, we would be happy to advise you with our expertise. Contact us so we can develop the optimal solution for your company together.




