In an increasingly dynamic and regulated financial world, the ability to respond quickly and accurately to change is crucial. As a senior consultant who has experienced SAP Profitability and Performance Management (PaPM) in numerous implementations, I see the solution not only as a tool, but as a strategic modeling platform. It was designed to provide management with accurate real-time calculations and ensure complete data governance across system boundaries.
SAP PaPM: More than just calculations
SAP PaPM is a flexible calculation and modeling platform with industry- and domain-independent variability and flexibility. It also enables companies to dynamically analyze and simulate complex financial and operational scenarios. The solution works in-memory and does not require its own data store – it accesses data directly from SAP S/4HANA, BW/4HANA, SAP Analytics Cloud, and non-SAP systems. In addition, SAP PaPM can be easily connected to user-friendly interfaces such as SAP Fiori, which significantly simplifies the operation of the system.
Key aspects of SAP PaPM:
- The architect of logic: PaPM is the central tool for mapping customer-specific use cases, utilizing comprehensive statistical and mathematical functions for high-performance calculations in the core.
- The seamless data integrator: The tool operates in-memory and avoids the need to create a separate data store. It accesses data directly – from SAP S/4HANA and BW/4HANA to non-SAP sources. This eliminates unnecessary replication.
- The governance enabler: Through central modeling and connection to Fiori interfaces, we improve the user experience and ensure the transparency and auditability of the business logic.
- The bridge builder: PaPM builds a bridge between controlling, IT, and the specialist departments. The graphical process mapping (as a cloud solution) makes even highly complex allocations comprehensible for all parties involved.
- The rule engine: We implement transparent, auditable business logic without traditional programming, which greatly simplifies maintenance and empowers the business departments.
SAP PaPM is therefore a flexible and high-performance calculation tool that supports complex, international business models in various industries (e.g., banking).
Our areas of focus
As a highly versatile tool, SAP PaPM can be used in numerous areas of application. As consultants, we focus on implementing strategic added value in the following areas:
Profitability & Controlling
- Detailed profitability analyses at the customer, product, and channel levels
- Compliance-compliant transfer pricing
- Highly accurate cost allocation (activity-based costing)
Planning & Simulation
- Dynamic “what-if scenarios”
- Strategic planning of HR costs, branch networks, and operating budgets
Sustainability & ESG
- Development of robust models for evaluating and reporting ESG metrics to meet new regulatory requirements
Technology & Integration
- Real-time processing of large amounts of data
- Fast, smooth integration into the existing SAP system landscape
Use case: Margin report – a look at how it works in practice
A classic example is the automated margin report. This report provides management with a central control tool for identifying profitable segments and hidden inefficiencies at the product, customer segment, branch, or region level.
Our approach with SAP PaPM:
- Data basis: We use join/view functions to seamlessly link revenues, costs, and customer data from various upstream systems (S/4HANA, BW, non-SAP)
- Processing: The core element is the allocation for transparent apportionment of indirect costs and the calculation for precise determination of gross and net margin figures.
- Added value & scaling: By fully automating margin reporting based on current data, we create the basis for dynamic “what-if scenarios” and support compliance with internal control regulations (e.g., according to MaRisk).
Extended use cases – even beyond the standard
In addition to classic applications, SAP PaPM is also suitable for less common scenarios in banking. One example is the planning and simulation of personnel costs – for example, to evaluate branch closures, the impact of bonus models, or strategic personnel relocation between locations. The ability to dynamically link internal HR data with financial key figures allows complex effects to be modeled and evaluated at an early stage – without rigid planning tools or complex Excel models.
Optimal integration with SAP S/4HANA
From a technological perspective, SAP PaPM unleashes its full potential in combination with SAP BW/4HANA. Deep technical integration allows us to use data models, hierarchies, and KPIs directly from BW and seamlessly process them in PaPM. The result: high-performance calculation models with complete traceability and centralized governance.
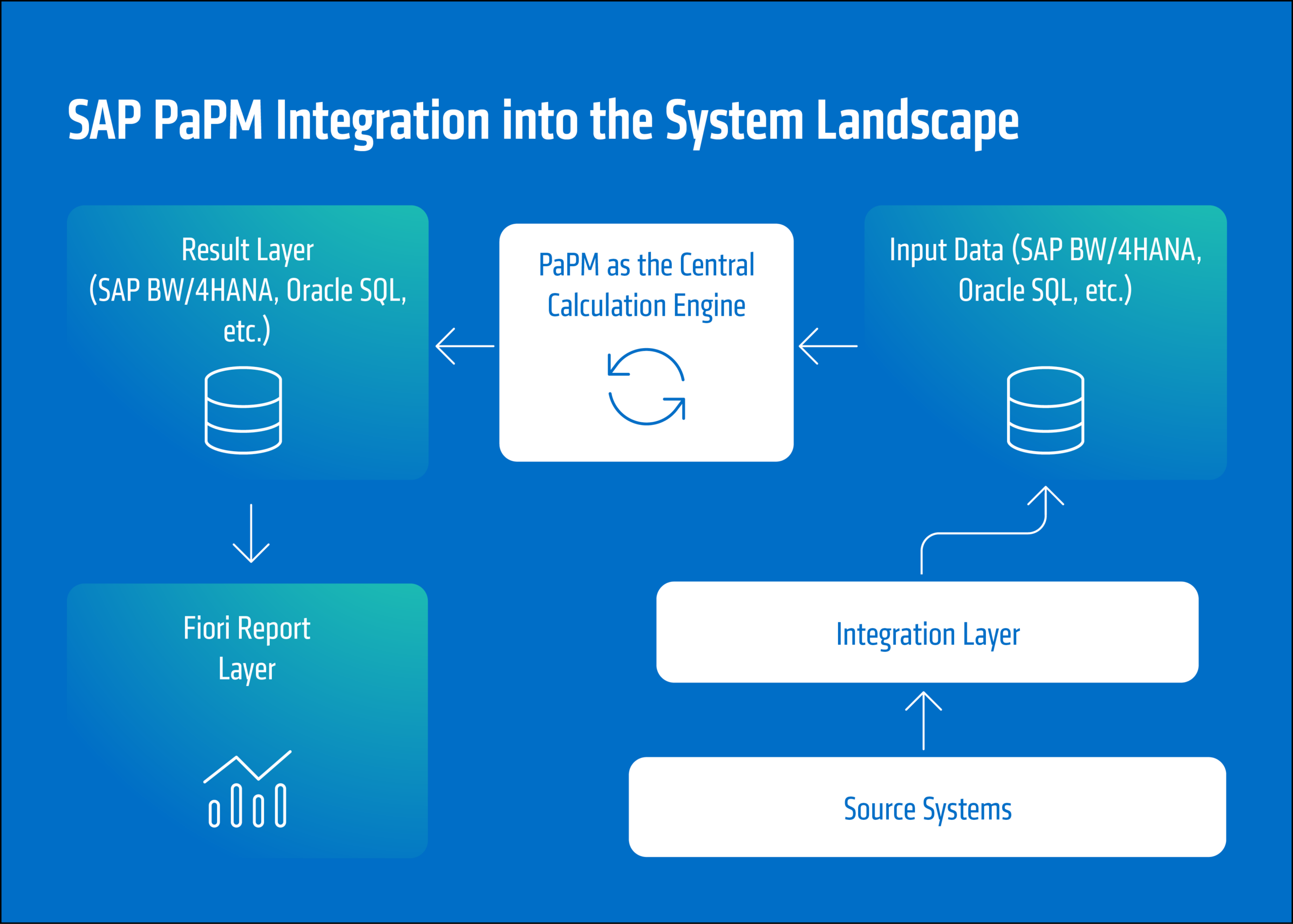
SAP PaPM can interact with other SAP applications via various interfaces such as SAP CDS views.
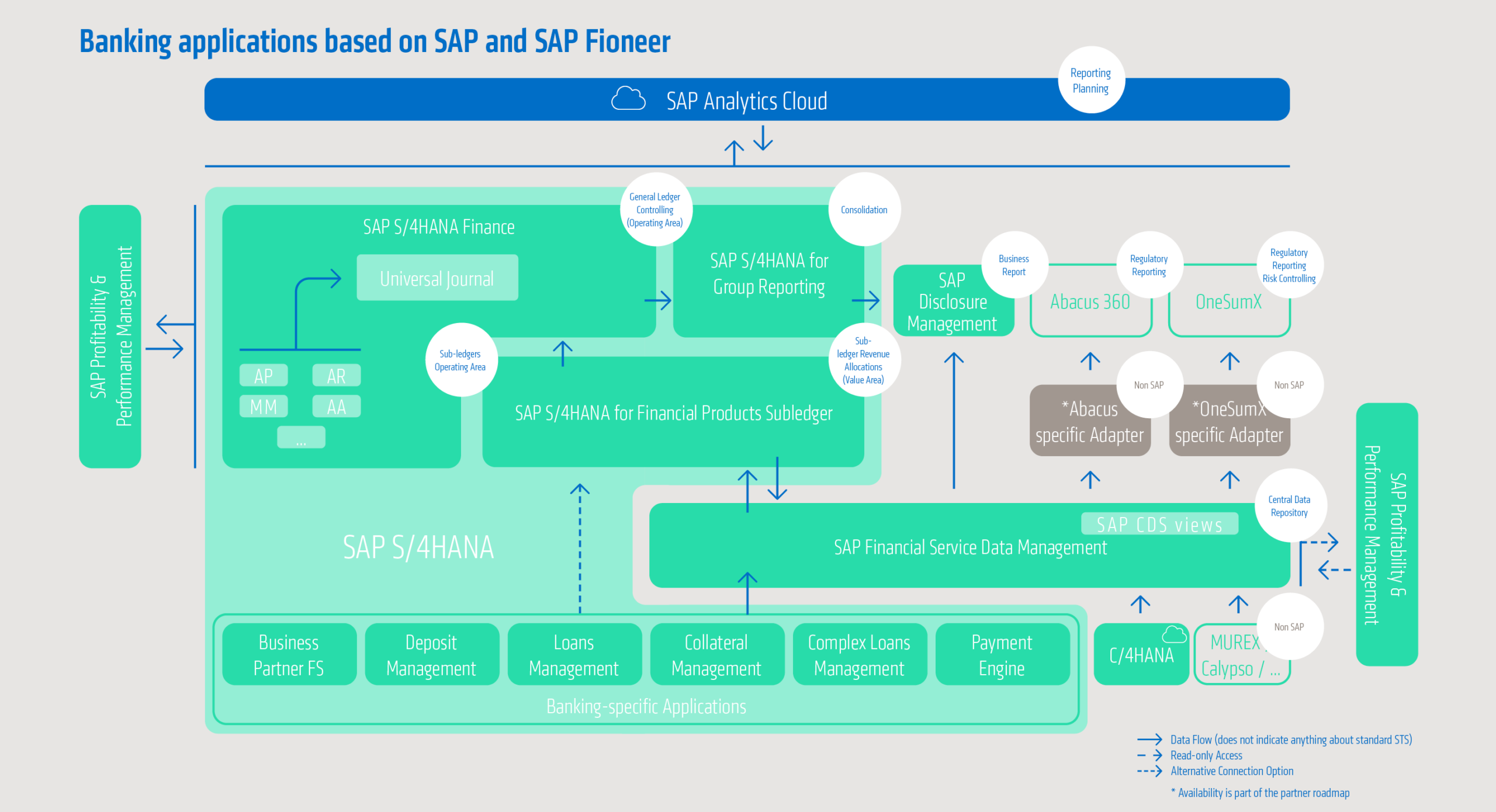
Functional diversity in SAP PaPM – a toolbox for data-driven control
SAP Profitability and Performance Management (PaPM) offers a wide range of functions that enable banks to map complex business and technical requirements precisely and flexibly. The modular structure of SAP PaPM allows you to combine specific function modules from a large number of options to suit your target architecture and data strategy.
The functions in PaPM can be divided into four main groups:
- Information functions, such as model tables, BW models, or file adapters, are used for the structured integration of external and internal data sources.
- Processing functions, such as calculation, conversion, allocation, or funds transfer pricing, enable the dynamic modeling of complex calculation logic – for example, for cost distribution, profitability assessment, or regulatory calculation.
- Write and adapter functions are used to write calculated results back directly to target systems such as SAP BW or SAP S/4HANA, for example via the Writer or Remote Function Adapter.
- Analytical functions, such as queries or machine learning, enable data preparation for reporting and analytical evaluations.

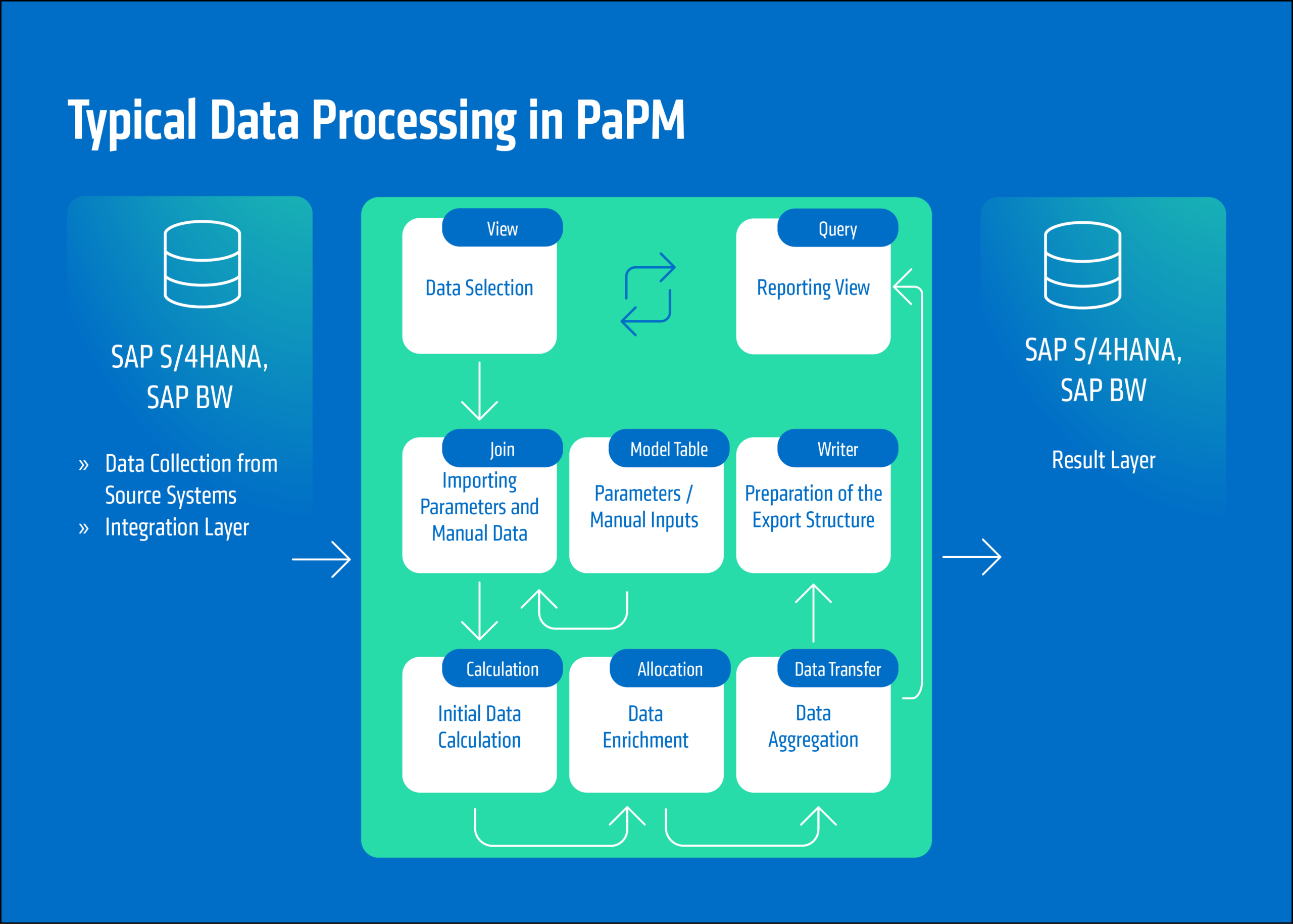
These function groups come together seamlessly in a typical data processing process – from the selection and parameterization of data to step-by-step refinement and structured output of results in SAP systems. Particularly noteworthy is the graphical and transparent process mapping in PaPM Cloud Version. This gives departments the opportunity to understand even highly complex models, comment on them, and adapt them independently if necessary.
For banks that work with large amounts of data, complex calculation models, and high regulatory pressure, SAP PaPM offers a strategic advantage: scalable data processing in real time with full integration into existing system landscapes.
More than just computing – additional functions for collaboration, control, and reporting
In addition to powerful data processing, SAP PaPM offers a variety of additional functionalities that are particularly important in the regulated and collaborative environment of a bank.
By assigning user groups, modeled environments can be managed in a differentiated manner and assigned to specific teams or roles, e.g., to separate test, integration, and production environments. This granularity enables secure and traceable collaboration between IT, controlling, and business departments.
SAP PaPM also impresses with its flexibility in the area of reporting. Data and results can be visualized either via preconfigured reporting views or by integration into SAC (e.g., dashboards), as well as exported directly to Microsoft Excel. The latter allows existing Excel-based control processes to be digitized step by step while simultaneously leveraging the advantages of a central platform – for example, in terms of data consistency, traceability, and performance.

Another key element is integrated process management. With the help of the “processes” in SAP PaPM, TEV (end-of-day processing) and MEV (end-of-month processing) processes, for example, can be triggered and monitored either automatically on a time-controlled basis or manually. This makes it possible to fully integrate and automate regular calculations – such as month-end closings or simulations – into the operational workflow.
These advanced capabilities make SAP PaPM not just a computing tool, but a complete platform for data-driven control and transparent collaboration in banking.
Conclusion and outlook
SAP PaPM is a game changer for banks seeking to transform their profitability management. It is not about replacing Excel, but about bringing transparency, flexibility, and scalability to financial management in a way that is , without having to resort to complex, difficult-to-maintain in-house developments.
From operational cost allocation to strategic simulations, PaPM delivers the answers—immediately, comprehensibly, and auditably. Are you ready to future-proof your bank management model and reap the benefits of a proven, scalable SAP tool?
adesso – Your partner for SAP PaPM and data management
As a long-standing SAP Gold Partner, adesso offers comprehensive services for SAP PaPM – from initial strategy consulting and proof of concept to technical implementation and go-live support. Our highly qualified experts have in-depth knowledge of both PaPM and the underlying systems. We support banks in the integration, modeling, optimization, and productive use of PaPM – in an agile, transparent manner and with a deep understanding of the industry. Talk to us. We will support you with expertise and passion.




