In the era of Industry 4.0, where the next-generation supply chain is shaped by the need for resilience and operational excellence, a manufacturing execution system (MES), coordinating shopfloor processes in the context of quickly evolving value-chains, is required. At the same time this MES needs to be able to fulfill the stringent requirements and challenges within the life science industry. While ME systems in general are already widely used in the life science industry for several years now, there is a need arising for systems with a modern core using cloud technology. When it comes to addressing those needs, SAP, as a pioneer in this area, provides a modern solution: SAP Digital Manufacturing (SAP DM). So, before we go into said challenges and needs, let’s quickly talk about what SAP Digital Manufacturing is.
What is SAP Digital Manufacturing?
SAP Digital Manufacturing is a cloud-based, data-driven shop-floor MES designed to optimize manufacturing processes through digitization and automation. It enables real-time monitoring, analysis, control and optimization of production operations. By leveraging data-driven insights, SAP Digital Manufacturing empowers organizations to streamline operations, reduce costs, and improve overall performance across the manufacturing lifecycle. As a Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) offering, SAP DM runs on SAP’s Business Technology platform (BTP) and seamlessly integrates into SAP’s landscape.
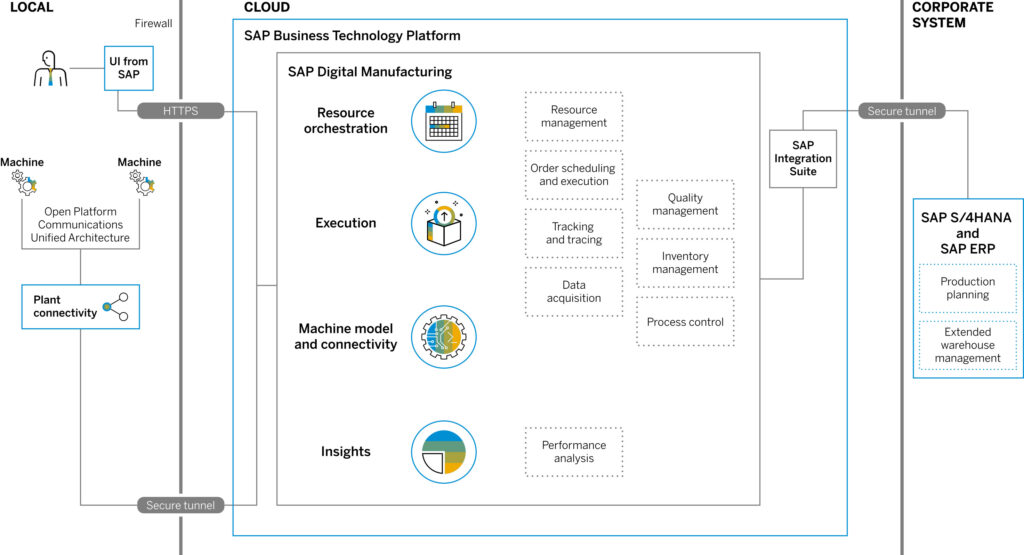
As part of SAP’s manufacturing digitalization strategy, SAP DM offers numerous benefits and new functionalities addressing some of the most urgent manufacturing challenges. Here are some of the key capabilities:
Manufacturing Execution
- Ability to monitor entire manufacturing process to optimize resources and execution
- Out-of-the-box integration to S/4HANA
- Integrated resource orchestration to manage shop floor workflow and labor assignments
- Connect shop floor machinery via Production Connector
Manufacturing Insights
- Cross plant and real-time analytics for manufacturing performance
- Redesign production operator dashboards by drag-and-drop functionality
- Monitor overall equipment effectiveness (OEE) and manage downtime events
Resource Orchestration
- Empower the control of shop floor operations and monitor events
- Schedule and dispatch operations to work centers and resources
What are the challenges with Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) in Regulated Industries?
In the area of life science, where precision, accuracy and compliance reign supreme, the adoption of new cloud technologies like SAP Digital Manufacturing holds immense promise. The life science industry operates within a highly regulated environment, where adherence to stringent quality standards and regulatory compliance is non-negotiable. Introducing new services in cloud environments, undergoing continuous release cycles, presents unique challenges:
GxP Compliance
GxP encompasses various regulations and guidelines that affect the entire lifecycle of pharmaceuticals and medical devices, including manufacturing, testing, inspection and distribution. SaaS solutions used in GxP-regulated environments must comply with GxP requirements, including data integrity, traceability, and auditability.
Compliance Requirements
Regulated industries must adhere to stringent quality management standards, such as ISO 13485, which governs the design, production, installation and servicing of medical devices and related services. SaaS providers need to demonstrate compliance with these standards to ensure the quality and reliability of their services.
Computer Systems Validation (CSV)
GAMP5 provides guidelines for validating automated systems in regulated industries, including pharmaceuticals and healthcare. SaaS solutions used in these industries must undergo rigorous validation processes to ensure compliance with GAMP5 standards and regulatory requirements.
Regulatory Changes and Updates
Regulatory requirements and cloud solutions with periodic updates, necessitate a high frequency of (re)validations. SaaS solutions must be agile and adaptable to accommodate those changes promptly, ensuring ongoing compliance and risk mitigation.
How is SAP addressing those regulatory challenges in life sciences?
Having obtained various certifications and attestations relevant in the life sciences sector, such as ISO 9001 and SOC2, SAP DM Cloud for Execution offers already a wide range of capabilities for the pharmaceutical industry including, but not limited to:
- E-Signatures to support compliance with 21 CFR Part11 regulation
- Extend Master Recipes integrated from S/4HANA with Work Instructions, Data Collections and Process Parameters
- Execute and Split Batch related Process Orders in the Production Order Dashboard (POD)
- Confirm process order phases with Yield, Scrap and Activities integrated with S/4HANA
- Record inspection results with Inspection Points integrated with S/4HANA QM
- View product history report for produced batches
From a regulatory compliance perspective, SAP DM offers a comprehensive working model that outlines its operational, technical, and functional scope. The functional scope outlines the key features needed in SAP Digital Manufacturing as a manufacturing execution system to support GxP-compliant manufacturing processes. While most of the underlying requirements are already provided by SAP DM, some features like Master Data Approval Management and Electronic Batch Records are still in development, but already part of SAP’s future roadmap.
Conclusion
SAP Digital Manufacturing is a comprehensive cloud-based ME solution designed to optimize manufacturing processes through real-time data analysis and automation. It integrates seamlessly with SAP’s ecosystem, providing capabilities for manufacturing execution, insights, and collaboration. While it offers significant benefits, particularly for highly regulated industries like life sciences, it also faces challenges related to compliance and validation. SAP addresses these by ensuring adherence to stringent standards such as ISO 9001 and SOC2.
SAP Digital Manufacturing is no longer a technology of the future – it’s here today. Many companies in the life science industry are already leveraging SAP DM to realize their journey towards smart factories. If we have piqued your interest and you would like to explore more about SAP Digital Manufacturing, don’t hesitate to get in touch with us anytime!




